Study hard
(c++)백준 2667번: 단지번호붙이기 본문
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2667
2667번: 단지번호붙이기
<그림 1>과 같이 정사각형 모양의 지도가 있다. 1은 집이 있는 곳을, 0은 집이 없는 곳을 나타낸다. 철수는 이 지도를 가지고 연결된 집들의 모임인 단지를 정의하고, 단지에 번호를 붙이려 한다. �
www.acmicpc.net
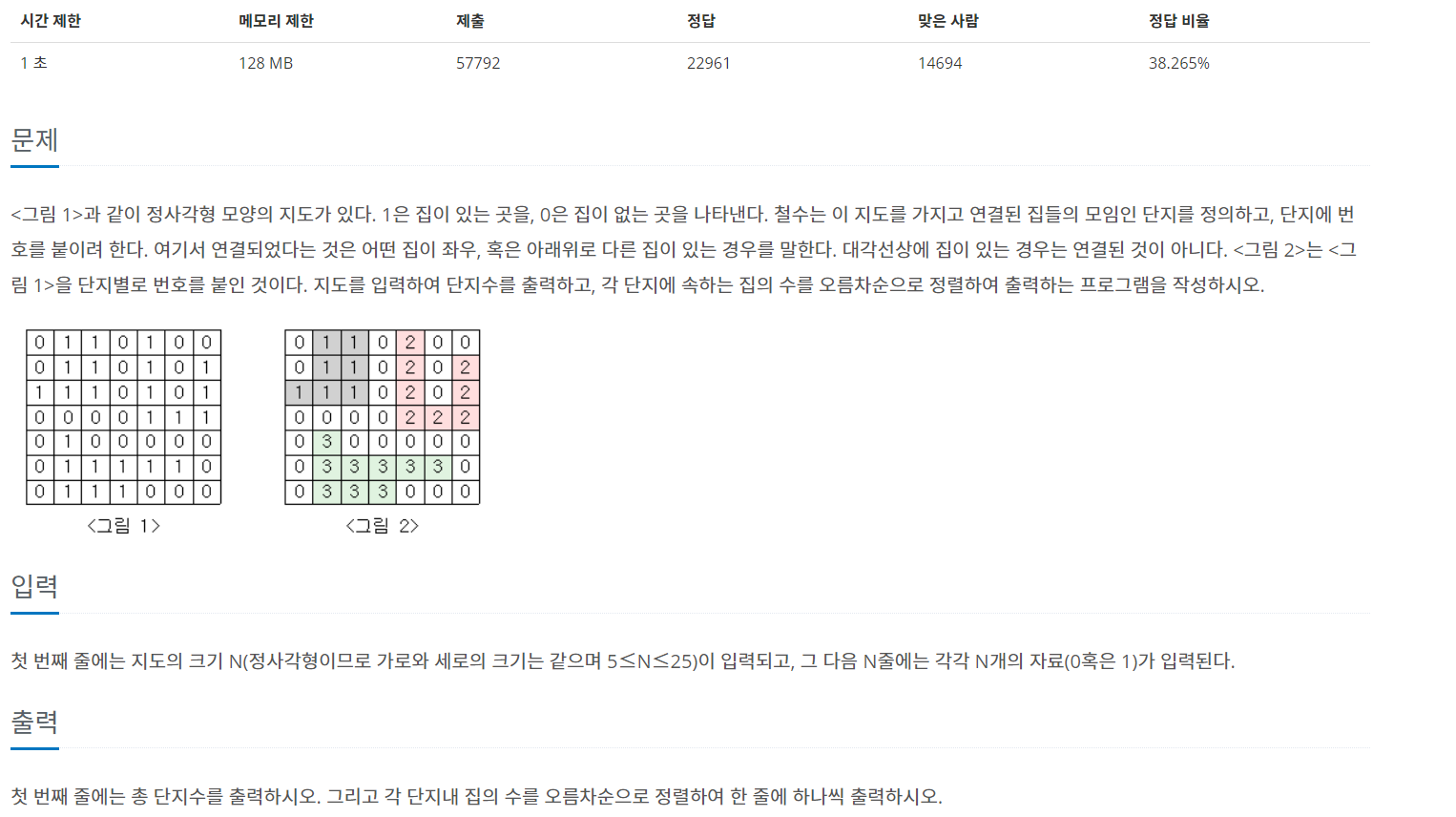
[풀이]
bfs탐색을 사용하여 풀었다.
그림처럼 단지마다 1,2,3 표시할 필요는 없고, 각 좌표의 상하좌우를 탐색해 이어져 있는 1의 개수를 구하면 된다.
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>//sort
#include <cstdio>//scanf
using namespace std;
struct Pos {
int x, y;//Map의 x좌표, y좌표
};
int N;
int Map[26][26];
bool visited[26][26];
const int dx[] = { -1,1,0,0 };//상하
const int dy[] = { 0,0,-1,1 };//좌우
void input() {
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
scanf("%1d", &Map[i][j]);//붙어 있는 숫자 중 하나만 받기
}
}
}
int bfs(int startx, int starty) {
queue<Pos>q;
visited[startx][starty] = true;
q.push({ startx,starty });
int cnt = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front().x;
int y = q.front().y;
cnt++;
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
//범위 확인
if (nx < 0 || nx >= N || ny < 0 || ny >= N)
continue;
//다음칸이 1이고, 아직 방문하지 않았으면
if (Map[nx][ny] == 1 && visited[nx][ny] == false) {
visited[nx][ny] = true;
q.push({ nx,ny });
}
}
}
return cnt;
}
void solution() {
input();
int Total = 0;
vector<int>v;//각 단지내 집의 수 저장
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (Map[i][j] == 1 && visited[i][j] == false) {
int home = bfs(i, j);
v.push_back(home);
Total++;//bfs할 때마다 단지 수 +1
}
}
}
cout << Total << endl;
//오름차순으로 정렬
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
cout << v[i] << endl;
}
int main() {
solution();
return 0;
}'백준 > bfs, dfs' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (c++)백준 7576번: 토마토 (0) | 2020.06.20 |
|---|---|
| (c++)백준 4964번: 섬의 개수 (0) | 2020.06.20 |
| (c++) 백준 9466번: 텀 프로젝트 (0) | 2020.06.19 |
| (c++)백준 2331번: 반복수열 (0) | 2020.06.19 |
| (c++)백준 10451번: 순열 사이클 (0) | 2020.06.19 |




